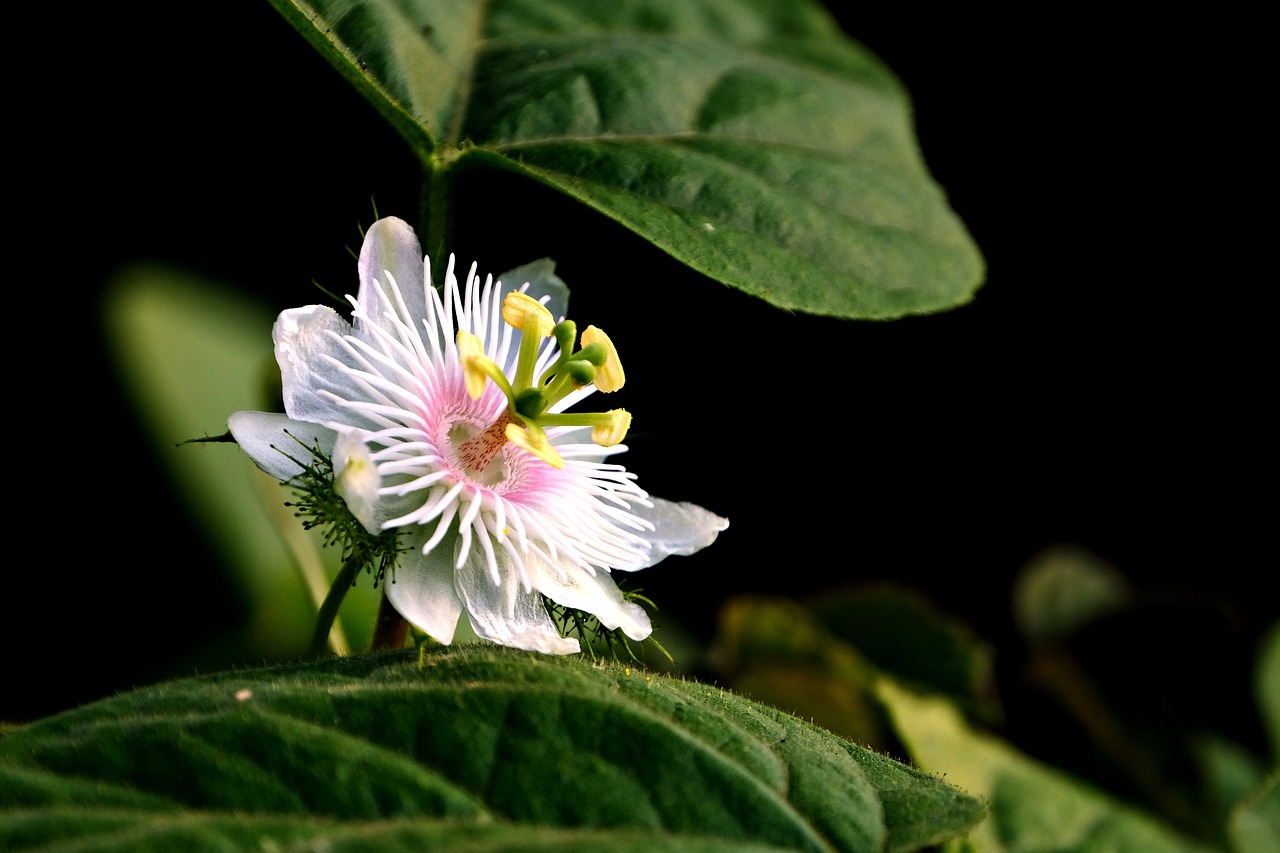
Passion Flower
Overview
The Passiflora, commonly known as Passion Flower, is a stunning vine famed for its vivid, intricate flowers and sprawling growth. Native to the Americas, it serves both ornamental and culinary purposes, thriving in a range of environments from lush gardens to heated greenhouses. Passion Flower can be grown for its beauty or its edible fruit, and contributes a tropical flair to any garden setting.

Characteristics
Known for its exotic and vibrant flowers, climbing growth habit, and historical symbolism related to the passion of Christ.
Region
Native to the Americas, found from Delaware to Missouri and south to Texas and Florida, as well as in Central and South America.
Natural Habitat
Passion Flowers are typically found in disturbed, fertile grounds such as fields and forest edges.
Cultivation
Thrives in full sun to partial shade, requires well-drained, fertile soil, and ample watering.
Uses and Benefits
Passion Flowers (Passiflora) offer multiple benefits beyond their stunning appearance. Not only are they cultivated for ornamental use, but certain species also produce edible fruits. Here’s a breakdown of how Passion Flowers can be utilized:
- Ornamental Value: The striking and exotic flowers make Passion Flowers excellent choices for garden display.
- Edible Fruit: Some species provide fruits that can be eaten fresh or used in recipes.
- Medicinal Uses: Extracts from the plant are used for their calming and sedative properties, aiding in sleep and reducing anxiety.3
Considering their variety and beauty, adding Passion Flowers to your garden or home can enrich your surroundings and well-being.

Cultivation Tips
For those eager to cultivate the vibrant Passiflora, here are some key tips to help them thrive:
- Sunlight: Passion Flowers require full sun to partial shade. Ensure they receive at least four to six hours of sunlight daily.
- Soil: Opt for rich, well-draining soil. Adding organic matter can enhance fertility and improve drainage.
- Watering: Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Regular watering is crucial, especially during dry periods.
- Support: Being climbing plants, they need structures like trellises or fences to support their growth.
- Pruning: Prune back in early spring to encourage new growth and maintain shape.
- Winter Care: In areas with cold winters, some types need to be overwintered indoors or provided with frost protection outside.
Successful cultivation also involves observing the plant for signs of stress or disease and addressing these promptly. With the right care, your Passiflora will produce stunning flowers and, in some cases, delicious fruits during the summer months1 2 5.
Companion Planting
Companion planting with Passiflora can enhance both aesthetic and ecological garden balance. Marigolds help deter pests naturally, while lemon balm provides a fragrant backdrop and attracts pollinators, crucial for fruit set in passion flowers.
For structural support, consider planting alongside sturdy shrubs or using trellises to assist their climbing nature 1 5. Engaging in such companion planting will not only optimize your garden’s beauty but also its productivity.
Seasonal Considerations
To ensure optimal growth and flowering of the Passiflora, seasonality plays a critical role. Here are key seasonal considerations for cultivating Passion Flower:
- Spring: Ideal time for planting. Ensure frost has passed and temperatures are warming.
- Summer: Peak flowering season. Provide regular watering and support for climbing vines.
- Fall: Begin to reduce watering. Prepare the plant for dormancy if in a cold climate.
- Winter: In colder regions, the plant may die back. Protect roots with mulch or move plants indoors if potted2.
Understanding these seasonal needs helps maintain a healthy and vibrant Passion Flower throughout the year.

Issues and Troubleshooting
Among the common issues faced by the Passiflora plant are pests like spider mites and aphids, which can sap the strength from the vine, affecting its growth and flower production.
To address pest problems, use mild insecticidal soap or neem oil applications, aiming to be environmentally friendly and maintain plant health.
Additionally, inadequate sunlight or water can hinder bloom and fruiting. Ensure your passion flower receives full to partial sunlight and enough water, especially during prolonged dry spells, to promote healthy growth and flowering.
History and Folklore
The Passiflora, or Passion Flower, boasts a fascinating history steeped in symbolism and storytelling. The term “passion” in its name originates from the Latin “passio,” which translates to suffering. This reference was made by Spanish missionaries who encountered the flower in South America during the 15th and 16th centuries; they interpreted the flower’s intricate structure as emblematic of the Passion of Christ—a sacred echo of the crucifixion and the associated suffering4. This rich tapestry of cultural and spiritual significance showcases the plant’s role beyond its biological attributes, intertwining nature with narrative.
References
1. “How to Grow and Care for Passionflowers | Gardener’s Path”, https://gardenerspath.com/plants/flowers/grow-passionflower/
2. “Passionflower: Plant Care & Growing Guide – The Spruce”, https://www.thespruce.com/passion-flowers-1403114
3. “Passion flower | Description, Species, Symbolism, & Facts”, https://www.britannica.com/plant/passion-flower
4. “Passion flower: How to plant, grow and care for passion flowers in the …”, https://www.houseandgarden.co.uk/article/passion-flower-plant-grow-guide
5. “How to grow passion flowers / RHS Gardening”, https://www.rhs.org.uk/plants/passion-flower/growing-guide
Image Credit: ignartonosbg
Image Credit: 652234
Image Credit: Couleur
Nicolas Duval
Nicolas is a passionate advocate for nature and the art of wildcrafting. His dedication shines through in Wildcraftia, a website he meticulously crafted to serve as a haven for nature enthusiasts worldwide. Driven by a deep appreciation for nature’s connection to humanity, Nicolas embarked on his journey in 2011 with SmokableHerbs, a platform showcasing his love for nature’s bounty. Building upon this foundation, he established Smokably, a thriving online store offering premium herbs and blends to a global audience.